- Appelez-nous au
86-013530516428 - Envoyez-nous un e-mail
sales@silveroptics.net - Whatsapp (en anglais seulement)
13530516428
Optical design involves the creation of systems or devices that manipulate light to achieve specific goals, such as forming images, focusing light, or dispersing wavelengths. Here's a general overview of the steps involved in optics design:
1. **Define requirements**: Understand the requirements and objectives of the optical system. This includes determining parameters such as wavelength range, field of view, resolution, focal length, and environmental conditions.
Optics Design
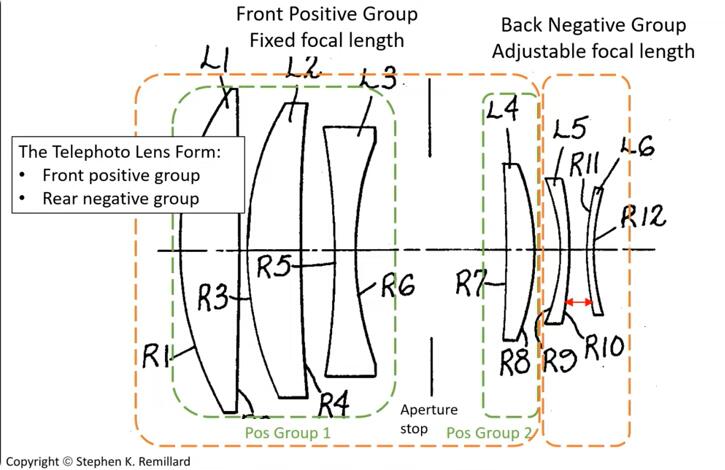
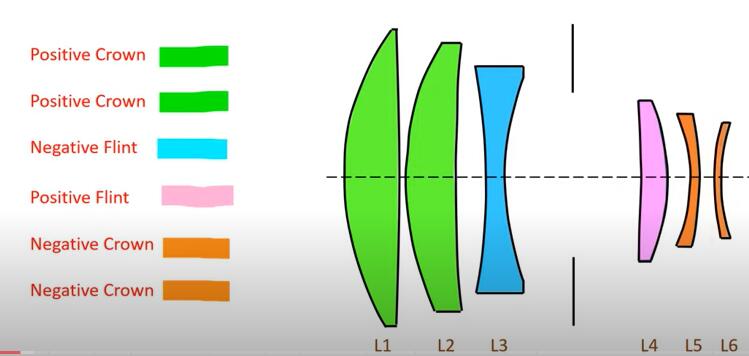
2. **Choose optical elements**: Select the appropriate optical elements (lenses, Miroirs, prisms, filters, etc.) based on the requirements of the system. Consider factors such as material properties, surface quality, and manufacturing feasibility.
3. **Design layout**: Determine the layout and arrangement of optical elements within the system. This involves deciding on the number, type, and positioning of elements to achieve the desired optical function.
Optics Design
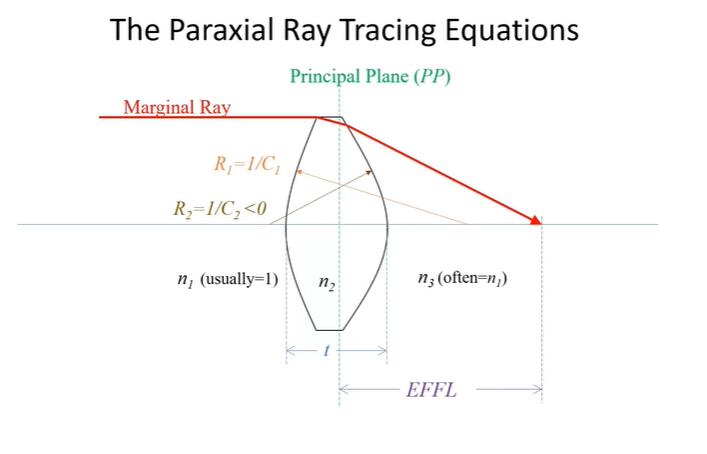
4. **Perform ray tracing**: Use optical design software to perform ray tracing simulations. Ray tracing helps predict how light rays will propagate through the optical system, allowing engineers to optimize the design for desired performance metrics such as image quality, aberrations, and efficiency.
5. **Optimize performance**: Analyze the results of ray tracing simulations and iteratively refine the design to optimize performance. This may involve adjusting parameters such as curvature, thickness, and spacing of optical elements to minimize aberrations and improve image quality.
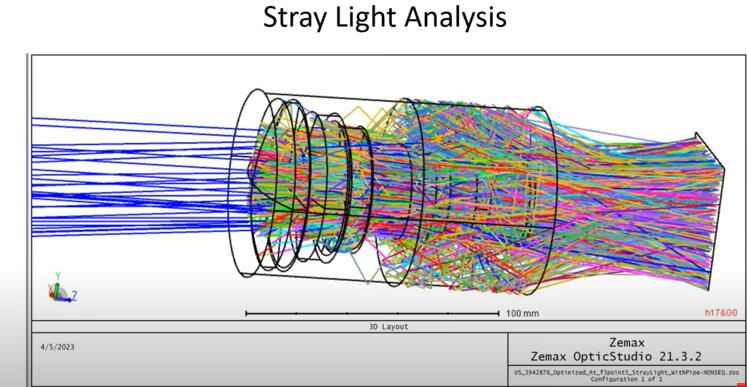
6. **Consider non-optical factors**: Take into account non-optical factors such as mechanical constraints, thermal effects, and stray light suppression. These factors can significantly impact the performance and reliability of the optical system.
7. **Prototype and test**: Build a prototype of the optical system and test its performance under real-world conditions. This may involve using optical test equipment to measure parameters such as resolution, contrast, and transmission efficiency.
Optics Design
8. **Iterate and refine**: Based on test results, iterate on the design to address any issues and further improve performance. This iterative process may involve making adjustments to optical elements, revising the layout, or refining manufacturing processes.
9. **Finalize design**: Once the design meets the requirements and performance goals, finalize the design and prepare it for production. This may involve documenting specifications, creating engineering drawings, and validating the design through additional testing.
10. **Manufacture**: Fabricate the optical system using appropriate manufacturing techniques and quality control measures. Ensure that components are manufactured to tight tolerances to maintain optical performance.
Optics Design
11. **Quality assurance**: Implement quality assurance processes to verify that manufactured optical systems meet specified performance criteria. This may involve inspection, testing, and calibration procedures to ensure consistency and reliability.
Throughout the optics design process, interdisciplinary collaboration between optical engineers, mechanical engineers, materials scientists, and other experts is often necessary to address the complex challenges involved in creating advanced optical systems.







